Self-Defense: How To Stay Cool In The Face Of Deadly Threats

Here we discuss some strategies for staying cool and ahead of fear when facing deadly threats.
It’s no secret that the coolest cucumber can think clearer and perform better in a violent physical altercation. Countless documentation of historical events has been written about the critical importance of staying cool under pressure, from Wyatt Earp to Kyle Carpenter. There are three things that can be done to keep your cool, should it hit the proverbial fan; listed in order of priority, they are: prepare your mind and body, map your environment and have an operational plan.
Humans need current information to make an accurate assessment and formulate a viable solution to a tactical problem. Anything other than relevant physical and mental input, rapid assessment, and a realistic solution can cause significant decision-making delays. In a life-and-death situation, even a few seconds of processing time can put you behind the action-reaction power curve.
If you expect to stay cool, you’ll need to allow that mind-body input-processing-solution process to run without a hiccup. There are two approaches to streamlining this process—one psychological and the other physical.
Psychological Preparation
Looking at it from the psychological perspective (mind), at times, your perception of a threat may be so intense that it could cause a “freeze response.” People who have experienced this have sometimes described accompanying physical symptoms such as tunnel vision, auditory exclusion, fine motor degradation, an inability to physically move and the like.
Most people are concerned about what they call being “frozen with fear.” However, you can effectively prepare for and overcome such a psycho-mechanical “freeze” both proactively (pre-freeze) and reactively (post-freeze).
Proactively, you can run through potential high-threat scenarios in your mind. The subconscious registers these imaginary vignettes no differently than if they were actual events. By watching these scenarios unfold in your mind’s eye, you gain a familiarity.
Reactively, you can take a deep resetting breath, and keep your eyes moving to break tunnel vision and gain continuous visual and audio input from your immediate surroundings. This causes your body to continue functioning on the conscious level and can help override the autonomic panic mechanism.
Speaking practically, what being “frozen with fear” more accurately describes is the brain being overwhelmed. The brain must process information to determine your best course of action. If that mental process is clogged, then you in effect are frozen, not with fear per se, but bogged down in a self-induced mental processing quagmire. Some call this analysis paralysis. The root cause is inbound information that may be new, unfamiliar, and threatening.
Proactively running mental self-rehearsals, engaging in force-on-force training, judgment exercises, and/or use-of-force training makes the experience no longer something new to your mind. Such proactive measures further mitigate information processing overload and decision paralysis by making such scenarios feel familiar.
Yes, from a psychological perspective there’s nothing much you can do about the “threatening” part, but you can certainly inoculate yourself against newness and unfamiliarity, which removes at least two-thirds of the mental processing roadblock. This is critical to prevent psycho-mechanical freeze.

Physical Preparation
Looking at it from a purely physical perspective (body), if you’ve never been in a face-in-the-dirt drag-down knock-out violent physical altercation, then such an experience would be a brand-new one to your body. You’d be unfamiliar with the nuances of physical combat. If you had experienced aggressive bodily impact prior, then it would no longer be new. If you were previously trained in boxing, martial arts or some other type of hard skill (physical training), your body would at least be familiar with certain aspects of aggressive physical contact such as how to best develop receiving or managing impact, make evasive movements, and other related body mechanics.
Training in hard skills is the most effective form of tactile inoculation available. It familiarizes you physically with the intricacies of personal combat. After you’ve rolled on the ground with someone trying to get you to tap out, stood toe-to-toe with someone trying to punch you in the throat, or spent quality trigger time on a firing range, your body begins to experience such activities as “just another day at the office.” Minus previous exposure, physical experience or familiarization, you place yourself at a tactical disadvantage. Real-world training in any hard skill is a recommended proactive measure that preps your body by preventing new and unfamiliar physical experiences from clogging mechanical function.
From a physical perspective, there’s nothing you can do about the “threatening” part of it in terms of physicality, but by training in any type of hard skill such as shooting, ground-fighting, boxing, martial arts and the like, you can gain a level of familiarity so that it’s no longer a new or unfamiliar physical experience.
Psychologically new and unfamiliar incoming information and physically new and unfamiliar experiences can cause a processing jam both in mind and body. Removing two out of the three roadblocks mentally and physically affords you a significant tactical advantage. You will be able to process a tactical solution faster (both mentally and physically) than those who would otherwise mechanically freeze.
It’s no surprise that the military and other government agencies (such as those providing protective services and the like) require rigorous psychological and physical training as a job prerequisite in preparing both mind and body.


Map Your Environment
Most people believe that situational awareness is just a matter of “looking around” or “keeping your head on a swivel.” It’s so common that these cliché lines can now be found in action-adventure movies. There’s a lot more to it than just simply looking.
How many times have you looked at your watch and then had to look at it again to take in the actual time? It’s not what you look at but what you see that matters. Looking is simply a matter of placing your eyeballs on something, whereas seeing is a matter of being mentally engaged with your environment.
Taking visual and audio control are the keys to mapping your environment. This valuable skill takes time to develop. Next time you go into a restaurant or a coffee shop or a store, take a minute to just stand off to the side for a second and look and listen for anomalies—those things that don’t seem to fit the environment. You may be surprised to find what you discover in this simple, easy-to-run exercise.
The second part of mapping your environment is to locate and identify your highest and most likely threat areas. These would include any structural entry or exit such as doors or windows. Commonly referred to as the “fatal funnel,” doorways, narrow halls and stairwells are natural choke points. You don’t want to find yourself stuck at a choke point in a violent physical altercation. Identify your choke points and how you would avoid them.
Lastly but certainly not least important in mapping your environment is identifying cover, concealment, fields of vision and fields of fire. Will that knee-high wall, table, or protruding structure stop a rifle round? Mapping your environment is a recommended active measure and something you can do on-site without anyone even suspecting what you’re doing.
Environmental mapping ties directly back to mind body prep in terms of interacting with your environment. Engaging with your immediate environment displaces any newness or unfamiliarity that may present itself within your surroundings, which further attenuates the probability of a psycho-mechanical freeze. Interacting with your environment both mentally and physically significantly contributes to formulating a layered solution to any burgeoning tactical problem.


Have A Plan
In the world of aviation, pilots always strive to be cognizant of the dangerous and cascading chain of events that can arise from simple oversight, negligence, laziness and overconfidence (complacency breeds contempt—that being the most inexcusable cause). These common operational blunders are the behaviors that generally lead up to an emergency. By being cognizant of these behavioral failures, pilots avoid ever having to implement the exigent response skills or reactive measures mandated annually in flight simulators.
The same applies to operational readiness. If you have taken proactive measures to prep your mind and body to neutralize the effects of processing new and unfamiliar information and experiences, you’re a step ahead of the next guy who has not. If you take the additional measure of mapping your environment, you’re then mentally engaged with and in further control of your immediate surroundings.
One more thing that you can do to help keep your cool should it hit the proverbial fan is to come up with an op plan. If the front door is no longer an option for you, then target your egress for the back door. Determine which pieces of cover you will employ and which route will get you there quickest with the least amount of physical injury.
Needing to keep cool means you’re physically reacting to an active threat with which you’re engaged. As it’s going down, take a deep cleansing breath to clear (or possibly unfreeze) your mind and plan your next move. Don’t just spin around in circles. You need to think on your feet.
Speaking of feet, staying mobile is a priority—moving targets are more difficult to hit than stationary ones. Staying mobile is the only way to create distance (which is your best friend) between yourself and the threat. More space equals more time, which equals more opportunity to solve the tactical problem.
Most folks think, I’ll just walk in and place my back against the wall so I can see what’s going on. OK, that’s not a bad initial idea, but then what? What’s your op plan if you do see something? Do you have an unimpaired field of vision? Where are the margins of your fields of fire should you need to go to guns? Do you even have a backstop? If it’s a no-shoot scenario, then to where is your first tactical movement?
If you had to move yourself and your family out the kitchen or back door, you’d need to get there incrementally in a full-blown firefight. How and where would you move to get to that next piece of cover? What are your safety options along the way?
You’ll most likely not be able to follow your initial op plan all the way to its terminal objective—Plan A hardly ever ends up working out—but even having one to start with puts you ahead of the power curve. You have saved the step of needing a plan. It’s always better to have and not need than need and not have.
Prepping your mind and body both proactively and reactively, mapping your environment by identifying ingress, egress, choke points, fields of vision, fields of fire and the like, plus having an op plan to follow during either a shoot or no-shoot scenario are the necessary gray man tools in your tool kit. They afford you the opportunity to gain the initiative, stay ahead of the action-reaction power curve and keep your cool when the mercury rises.
Quick Tips To Not Lose Your Sh!T
Catch A Breath
One of the first signs of panic is how you’re breathing, and it’s directly tied to how your heart is beating. Often breath gets quicker in an effort to increase blood oxygenation but very quickly this can spiral into losing consciousness. Other times, the breath may be unknowingly held in a losing attempt to slow the heart, and this has the exact same result.
If you’re going to maintain your decision-making conscious brain, you need to manage your heart. And to do that, you need to control your breath.
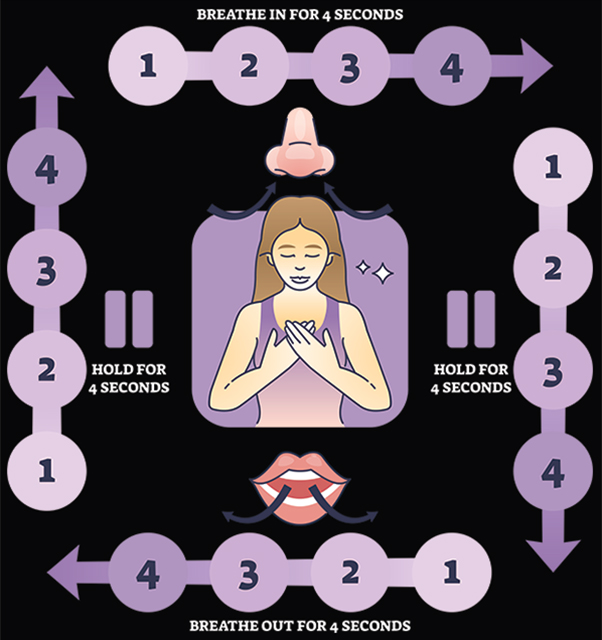
Breathing exercises are not just for yoga studios, and this technique has been used by special units for decades. The most basic is called the Box Breath or 4-Count Breathing. Like a box, it has four steps:
- Inhale slowly while counting to four. Let your stomach expand and feel the breath come in.
- Hold your breath for a count of four (this one can be the most difficult).
- Exhale to a count of four, emptying your lungs if possible.
- Repeat.
This technique seems simplistic, but it can be difficult to perform under pressure unless it’s practiced. Use your mind to resist the urge to hyperventilate, assure your body it is getting enough oxygen. Give it a try during physical exercises and as you go about your day until it becomes second nature. Some advocate the breath coming in the nose and out of the mouth but none of that matters so long as you’re controlling the pace of your breath. There are also variations in counts from different yoga practices, and those are likely fine too.

Use Your Senses
You can avoid “getting sucked in” and over-focusing on a perceived threat, or break yourself free from tunnel vision, by intentionally engaging your senses. This helps keep you grounded, and the easiest way is to actively identify objects or features with each.
In order of typical effectiveness:
Look
Physically move your head from one side to the other to break tunnel vision. Identify two or three objects by calling them out—out loud and to yourself if necessary. Reading signs and locating doorways are easy buttons.
Listen
If you’ve just been in an explosion or gunfight, this one can be tough. Still, actively try to identify environmental sounds. Just as before, single them out to ensure you’re actually paying attention.
Touch
Some people will lose the feeling in their fingers, hands, and feet when panic rises. You can help combat this by rubbing your fingers or hands together. Touching a wall, the texture of your clothes, or other exposed parts of your skin.
Editor’s Note: This article originally appeared in the February 2025 issue of Gun Digest the Magazine.
More Knowledge For The Armed Citizen:


Next Step: Get your FREE Printable Target Pack
Enhance your shooting precision with our 62 MOA Targets, perfect for rifles and handguns. Crafted in collaboration with Storm Tactical for accuracy and versatility.
Subscribe to the Gun Digest email newsletter and get your downloadable target pack sent straight to your inbox. Stay updated with the latest firearms info in the industry.







